Education
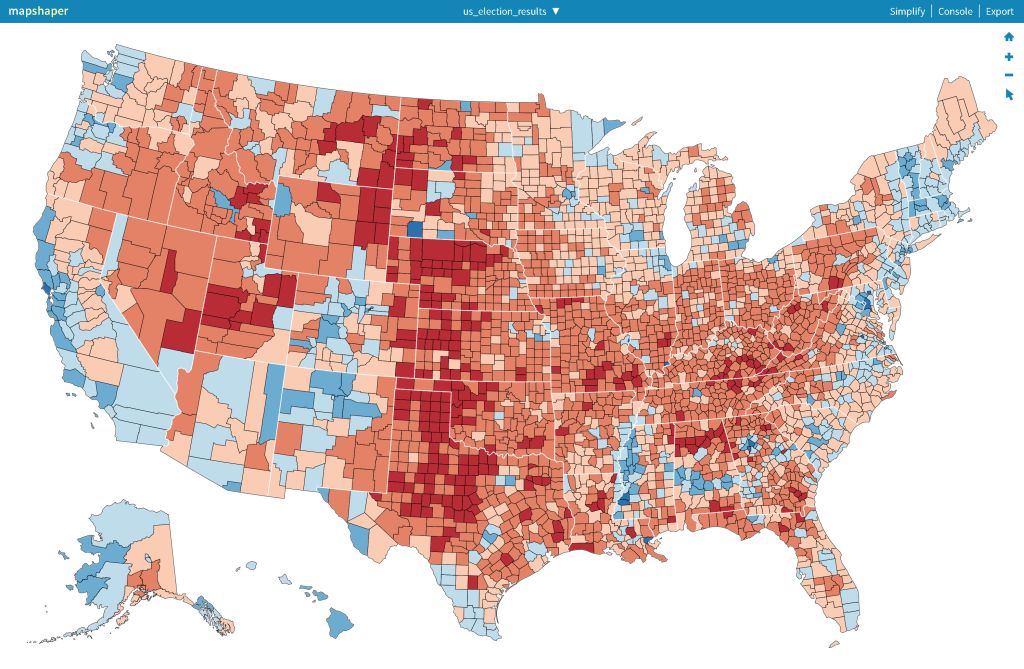
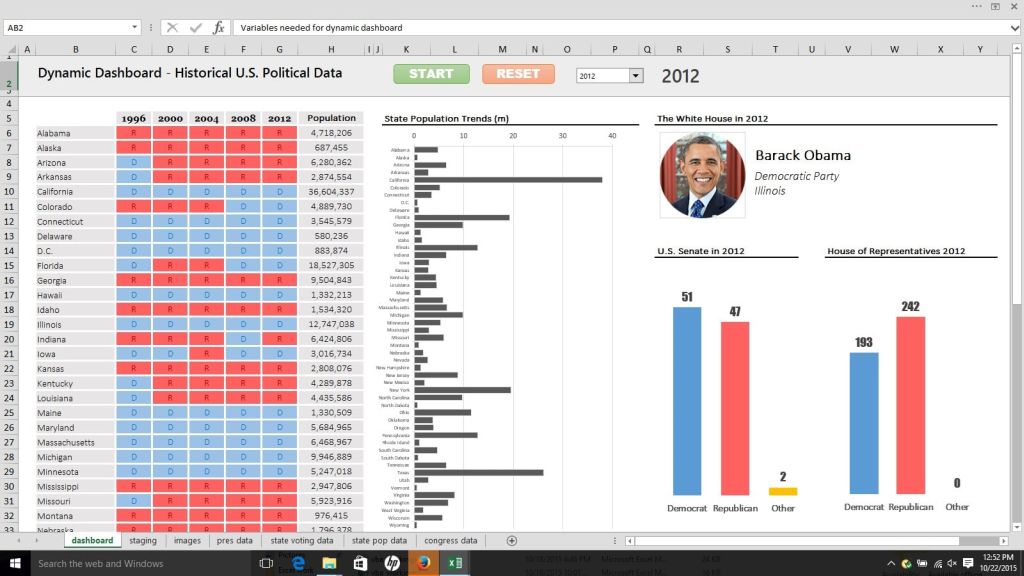
Streamlining Election Vote Counting with an Excel Election Template
Summary: The blog summarizes the methods to repair MS Excel workbook and explains various benefits that each procedure offers. It also describes a third-party Excel Repair tool for a successful recovery of data from 0 KB Excel file error message (when excel file size become 0 kb).
While attempting to access Excel workbook, if you encounter an 0 KB file error message (excel file size become 0 kb), the chances are that your file is corrupt or the version of the file you use is not compatible with the Excel edition. The error message reads as follows:
“Excel cannot open the file ‘filename.xlsx’ because the file format for the file extension is not valid. Verify that the file has not been corrupted and that the file extension matches the format of the file.”
Excel provides a few troubleshooting procedures that users may execute to repair the workbook. These workaround methods are easy to execute; however, doing so may also lead to permanent loss of data unless you are technically adept. Before following any of the recovery methods, it is recommended that you create a backup of your Excel file.
Method #1: Excel File Recovery Mode
MS Excel automatically starts File Recovery mode upon opening, when any corruption is detected in the Workbook. You can also follow the manual procedure to open the File Recovery mode if it doesn’t start automatically.
Follow the steps below to manually start the File Recovery mode:
- Click on the File tab and then click on Open
- Click the folder where the corrupt file exists
- In the Open dialog box that appears, select the damaged workbook
- Click on the arrow button available next to Open button and select Open and Repair
- To repair maximum data from the corrupt workbook, click on Repair
If Repair fails to recover the data, select Extract Data for extracting formulas and values from the Excel workbook.
Method #2: If Workbook Opens in Excel
Revert Workbook to the Last Saved Version
In case the Workbook turns corrupt while working on it, you may not be able to save the changes. In such a scenario, you can revert the Workbook to last saved or the previous version. To do so:
- Click on File and then click on Open
- Double-click on the Workbook name
- Next, click Yes to reopen
Note: You may lose the changes made recently to the Workbook as it will open without any changes that have turned Workbook corrupt.
Method #3: When Workbook Cannot Open in Excel
Set Calculation Option to Manual
If you are not able to open the Workbook in Excel, then attempt to change the calculation setting to manual from automatic as it may open in Excel as it cannot be recalculated thereafter.
- Click on the File tab and then click on New
- Click on the Blank workbook available under New
- Next, click on File and then select Options
- Under Calculation Options in the Formulas category, select Manual and then OK
- Next, click on File and then click on Open
- Search and find the corrupt Workbook and then double-click to open
Method #4: Use External References
You may try using external references to link to the damaged workbook; however, it will help retrieve only data from the Workbook. Other contents such as calculated values and formulas can be dropped for retrieval. The entire procedure to use external references to links to the corrupt workbook is considerably complicated and hence requires someone with a good technical know-how.
Method #5: Save from Backup
If a backup is available, you can access your lost data if the workbook turns corrupt. To automatically restore the backup, follow the steps below:
- Click on File and then click on Save As
- Click on Computer and select the Browse button
- In the then appeared Save As dialog box, select the arrow sign available next to the Tools button. Then select General Options.
- In the General Settings dialog box that appears, check the box associated with Always create backup box
Method #6: Third-Party Recovery Assistant
You may also opt for third-party applications to resolve your Excel file 0KB issue. Not only would they resolve all types of XLS and XSLX issues, but their easy to use interface allows for a seamless recovery. Stellar Phoenix Excel Repair is one such software. With it, you can simply repair the file from any type of corruption, from smaller to a higher level. All the contents of the Excel workbook such as charts, rules, properties, texts, engineering formulas, etc. can be restored back on the machine effortlessly.
The recovery procedure is simple to execute. This Excel Repair software can be run on all the versions of Windows OS. It supports all versions of Excel, from the oldest to the most recent editions.
The tool is simple to execute and doesn’t require you to have any specific technical expertise. It easily resolves the 0KB Excel file issue and retrieves the corrupt data. All recovered data is saved in a new file at the desired location while the older files remain intact.
The Way Forward
MS Excel is an indispensable part of a professional day-to-day life. With it, managing and analyzing data to support your decision-making and other business outcomes becomes easy. Therefore, its importance cannot be discounted. It is always recommended to take preventive measures to safeguard your Excel files from turning corrupt; however, if it becomes corrupt, then employing a secure and reliable tool is recommended.
Education
From SEO to Influencers: How Supplement Brands Market Effectively
The health and wellness industry are thriving, and supplement brands are at the forefront of this growth. But how do these brands stand out in a crowded marketplace and build consumer trust? The secret lies in strategic marketing.
From leveraging the power of search engine optimization (SEO) to forming authentic connections through influencers, successful supplement brands use a mix of tactics to capture attention and convert interest into sales. Here’s a closer look at how these strategies work and what you can learn from them.
The Power of SEO in Driving Organic Traffic
Search engine optimization (SEO) is one of the most cost-effective ways to attract customers to your website. By optimizing your site for specific keywords like “best protein powder” or “natural vitamin D supplements,” or “cjc-1295 dac 10mg”you can rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). This helps drive organic traffic, bringing potential buyers directly to your virtual doorstep.
Take Garden of Life, for instance. This supplement brand has built a highly effective SEO strategy by publishing blog content that answers health-related questions consumers often search for. Articles like “The Benefits of Probiotics” educate consumers and improve the brand’s visibility on Google. By providing helpful, keyword-optimized content, Garden of Life strengthens its credibility while driving traffic to its site.
The first step for brands looking to boost their SEO is conducting thorough keyword research using tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush. Once you’ve identified high-impact keywords, optimize your website’s meta titles, descriptions, and blog posts. Don’t forget to focus on technical SEO as well, make sure your site is fast, mobile-friendly, and easy to navigate.
Building Trust Through Influencer Marketing
Influencers have become a huge force in the supplement market. Why? People trust influencers. When a fitness trainer or wellness advocate recommends a product, their followers are likelier to believe it’s worth trying. Influencers bridge the gap between brands and consumers, offering a sense of authenticity that traditional ads often lack.
Consider Athletic Greens, a greens powder brand that’s mastered the art of influencer marketing. The brand has built significant credibility by partnering with popular podcasters, fitness enthusiasts, and lifestyle influencers. These partnerships often involve honest product reviews, testimonial-style posts, and discount codes, which excite consumers to try the product.
Finding someone whose values align with your brand is the key to effective influencer marketing. Micro-influencers, who typically have between 10,000 and 100,000 followers, can offer higher engagement rates than celebrity influencers. For example, a yoga instructor with a small but loyal following may create a more genuine connection with your target audience than a world-famous athlete.

Content Marketing That Educates and Converts
Content marketing goes hand in hand with SEO but deserves its spotlight. A well-crafted blog, eBook, or video can build brand authority and nurture leads. The key is to provide value to your audience.
For example, brands like NOW Foods publish well-researched guides on topics like “How to Choose the Right Supplements for Your Goals.” This establishes NOW Foods as an authority and helps consumers make informed decisions, earning their trust in the long run.
Beyond blogs and guides, long-form video content can showcase how your products fit into consumers’ lives. Recipe videos featuring protein powders or step-by-step tutorials on creating a supplement routine can add an extra layer of engagement. Visual content, such as infographics and branded animations, can also make more complex scientific information—like the benefits of omega-3 fatty acids—digestible and shareable for your audience.
Leveraging Email Marketing for Retention and Upsells
Email marketing remains a vital tool for supplement brands. It’s not just about acquiring new customers; it’s about keeping existing customers engaged and loyal. Emails allow you to promote seasonal sales, share valuable health tips, and introduce new products.
Take Ritual, a subscription-based supplement brand. Ritual creates personalized emails catering to users’ specific health goals. They send regular updates, friendly reminders about subscription renewals, and educational content about what goes into their vitamins. This nurturing approach makes customers feel like more than just a transaction.
To get started with email marketing, invest in tools like Mailchimp or Klaviyo to create automated campaigns. Always segment your email lists to send the right message to the right audience. For example, customers who recently bought a pre-workout supplement might appreciate tips on optimizing their fitness routines.
Social Media Advertising to Broaden Reach
Social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok provide fertile ground for advertising supplement goods. Facebook ads allow you to target users based on their interests, while Instagram Stories can use eye-catching visuals to highlight your product. TikTok, on the other hand, provides opportunities to go viral with creative, relatable content.
OLLY, a vitamin brand known for its colorful packaging, has expertly used Instagram to showcase its playful brand personality. Their mix of vibrant visuals, customer testimonials, and educational posts create an engaging presence that attracts new buyers daily.
For effective social media advertising, experiment with formats like carousel ads, allowing you to feature multiple products simultaneously. Use user-generated content (UGC) to amplify social proof and be sure to monitor performance metrics to tweak campaigns as needed.
Education
How to Ungroup Pivot Table Fields in Excel and Enhance Your Data Analysis

Pivot tables are one of the most powerful tools in Excel, enabling data analysts and business owners to organize and summarize large datasets into meaningful insights. However, the grouping of fields within pivot tables can sometimes limit the depth and flexibility of analysis. Knowing how to ungroup fields when necessary can unlock new analytical opportunities and improve decision-making.
This guide explains what grouped and ungrouped pivot table fields are, demonstrates how to ungroup them in Excel step by step, and provides real-world scenarios where ungrouping fields can transform your analysis. Additionally, you’ll find tips for efficiently using pivot tables, ensuring accuracy in your business insights.
What Are Pivot Table Fields and Why Are They Grouped?
Pivot tables are designed to summarize, analyze, and present data in a way that simplifies decision-making. They allow users to group and aggregate data into meaningful categories. For example, sales data can be grouped by years, months, or regions to provide a high-level overview.
A grouped field in a pivot table is when Excel combines values into categories. For instance, if you have transactional dates, Excel might automatically group them into months or quarters. While grouping can simplify the presentation, it can sometimes hide granular details that are critical for certain analyses.
An ungrouped field, on the other hand, retains the raw dataset without aggregation. This offers more flexibility, particularly when analyzing each data point or creating custom groupings suited to your specific needs.
Why Ungrouping Pivot Table Fields May Be Necessary
While grouping provides clarity, it can restrict the ability to perform detailed data segmentation. Here are some situations where ungrouping pivot table fields is beneficial:
- Detailed trend analysis: If examining daily instead of monthly trends, ungrouped data offers greater granularity.
- Customized grouping: Ungrouping fields enables analysts to create custom categories that better reflect unique business needs.
- Avoiding data distortion: Aggregated groups may obscure unusual but important data points, such as outliers or spikes.
By ungrouping, you regain control of the data and can tailor it precisely to the goals of your analysis.
How to Ungroup Pivot Table Fields in Excel
Ungrouping pivot table fields in Excel is straightforward. Follow these steps to fine-tune your data presentation and analysis:
Step 1: Open Your Workbook and Select the Pivot Table
Open the Excel workbook that contains your pivot table. Click anywhere within the pivot table to activate the “PivotTable Analyze” menu on the ribbon.
Step 2: Identify the Grouped Field
Determine which field you want to ungroup. This could be a specific date field grouped into months or quarters, or numeric data grouped into ranges.
Step 3: Ungroup the Field
- Click on any cell within the grouped field.
- Navigate to the ribbon and select the “PivotTable Analyze” tab (called “Analyze” in older Excel versions).
- Click “Ungroup” in the Group section of the ribbon. Alternatively, right-click on the grouped field and choose “Ungroup” from the dropdown menu.
Step 4: Verify Your Data
After ungrouping, the field will display the individual data points instead of categories. Review the pivot table to ensure it reflects the intended changes.
Step 5: Refresh Your Pivot Table (if necessary)
If working with dynamic data sources, refresh the pivot table to apply the ungrouping to all relevant data. To do this, right-click anywhere in the table and select “Refresh.”
That’s it! Your grouped field is now ungrouped, giving you the precision you need for your analysis.
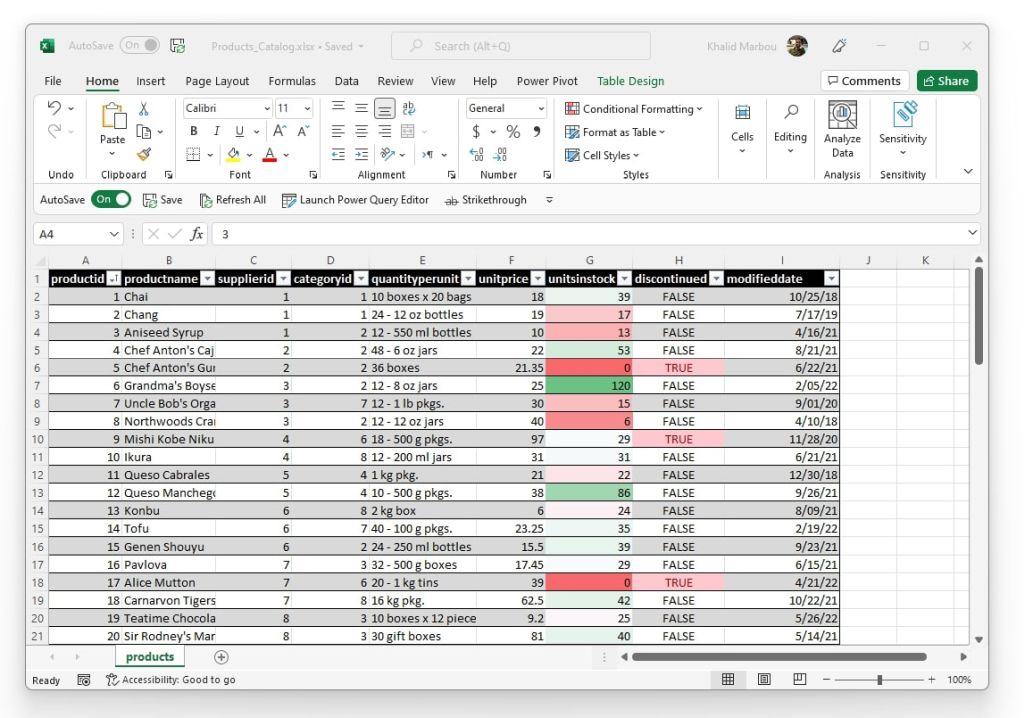
Real-World Examples of Ungrouping Pivot Table Fields
To understand the value of ungrouping fields, consider these scenarios where it can enhance analysis and decision-making:
- Sales Trends
A retail company wants to analyze sales performance by day rather than by month to identify precise dates of promotions or product launches that led to spikes in sales. Ungrouping the date field provides the needed granularity.
- Revenue Analysis by Region
A business owner initially groups revenue data by state to get an overview but decides to ungroup it to pinpoint revenue from individual cities for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Inventory Review
A supply chain manager grouped product stock by range (e.g., 1-10, 11-20) but needs to ungroup it to evaluate the specific inventory levels of individual items and plan reorders more effectively.
These scenarios demonstrate how ungrouping pivot table fields can help tailor analysis to specific goals and contexts.
Best Practices for Working with Pivot Tables
For data analysts and business owners, efficiency and accuracy are crucial when using pivot tables. Follow these expert tips to make the most out of your pivot table analysis:
1. Plan Your Analysis Goals Before Grouping or Ungrouping
Define what insights you need to extract from the data. This helps determine whether to group or ungroup fields.
2. Use Clear Naming Conventions
Rename fields and group labels for clarity. Descriptive names such as “Q1 Sales” or “East Coast Revenue” make pivot tables easier to read and interpret.
3. Leverage Filters for Deeper Analysis
Use built-in pivot table filters to focus on specific data subsets without having to ungroup unnecessarily.
4. Keep a Copy of the Original Data
Before ungrouping, always retain a backup of the original pivot table. This ensures you can revert to the earlier format if needed.
5. Refresh Your Data Regularly
Ensure your pivot table always reflects the latest data by refreshing it after making changes or ungrouping fields.
6. Explore Advanced Customization
Combine ungrouped data with calculated fields or custom sorting to unlock deeper insights tailored to your business needs.
Unlock Better Insights by Ungrouping Pivot Table Fields
Ungrouping pivot table fields in Excel provides data analysts and business owners with the flexibility to perform more detailed and tailored analyses. By understanding when and how to ungroup fields, you gain greater control over your data, enabling improved decision-making and more precise insights.
Whether you’re tracking sales trends, analyzing regional performance, or optimizing inventory, mastering this skill ensures your pivot tables work for you—not the other way around.
Are you ready to start making better use of your data? Open Excel, ungroup those fields, and take your data analysis to the next level today!
Meta Data
Meta title: How to Ungroup Pivot Table Fields in Excel
Meta description: Master ungrouping pivot table fields in Excel. Enhance your data analysis and make tailored decisions with this simple step-by-step guide.
Education
Chart With High and Low Values

When one value on your chart is much higher than the rest, lower values on your chart might become unreadable. In this tutorial, you will learn a net way to deal with this kind of situations.
As you see, smaller values are almost indistinguishable due to chart scaling to show all values together.
We want to show all values together in the same chart too, but we also want them to be clearly understandable. Therefore, we have to crop this towering value to make it scalable.
To achieve our goal, we need to make a couple of little adjustments to our data set:
- Add 3 columns next to our original data. First column values will be the same for each series except the one with the high value. Give it a value just a little higher than the second higher value.
- Second and third columns will have “=NA()” as values for all series except the one with the high value. For second column, give it a value that will create a gap. And for third column, give it a little bigger value but not bigger than the first column value.
- Insert a stacked column chart by selecting whole data, than uncheck “Production” series from your source list.
- Your chart is supposed to look like the one in the picture below.
- Now we are going to format this chart to mate it look like the one below:
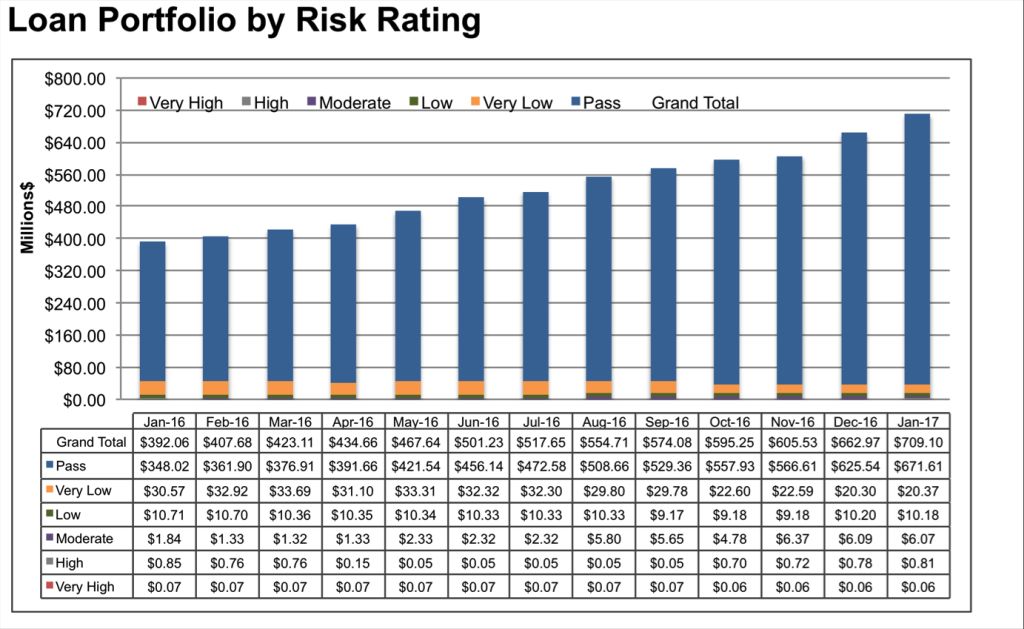
Here are the formatting I made on my chart:
- Add a chart title.
- Change color of the third column value on the chart to match the color of other series.
- Change fill of the second column value on the chart as pattern fill. Select vertical lines as pattern.
- Add labels for the first column values and move them above the bars.
- Add a label to the top of he longest series as a test box and write the original high value in it.
This is an easy way to create a chart with high and low values which shows all values together without compromising readability.
-
 Education11 months ago
Education11 months agoExcel Sunburst Chart
-
 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoFix Microsoft Excel Error – PivotTable Field Name Is Not Valid
-

 Excel for Business8 months ago
Excel for Business8 months agoInteractive Excel KPI Dashboard
-

 Education12 months ago
Education12 months agoPositive Negative Bar Chart
-

 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoExcel Gantt Chart (Conditional Formatting)
-
 Excel for Business1 year ago
Excel for Business1 year agoMastering Chart Elements in Excel to Unlock Better Data Visualization
-

 Education12 months ago
Education12 months agoWord Cloud Generators: The Modern Tool for Simplifying Data Visualization
-
 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoStreamlining Election Vote Counting with an Excel Election Template